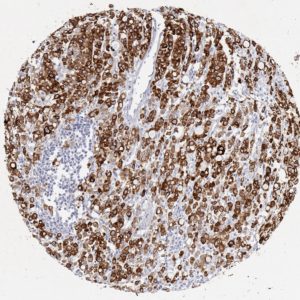
Reactivity
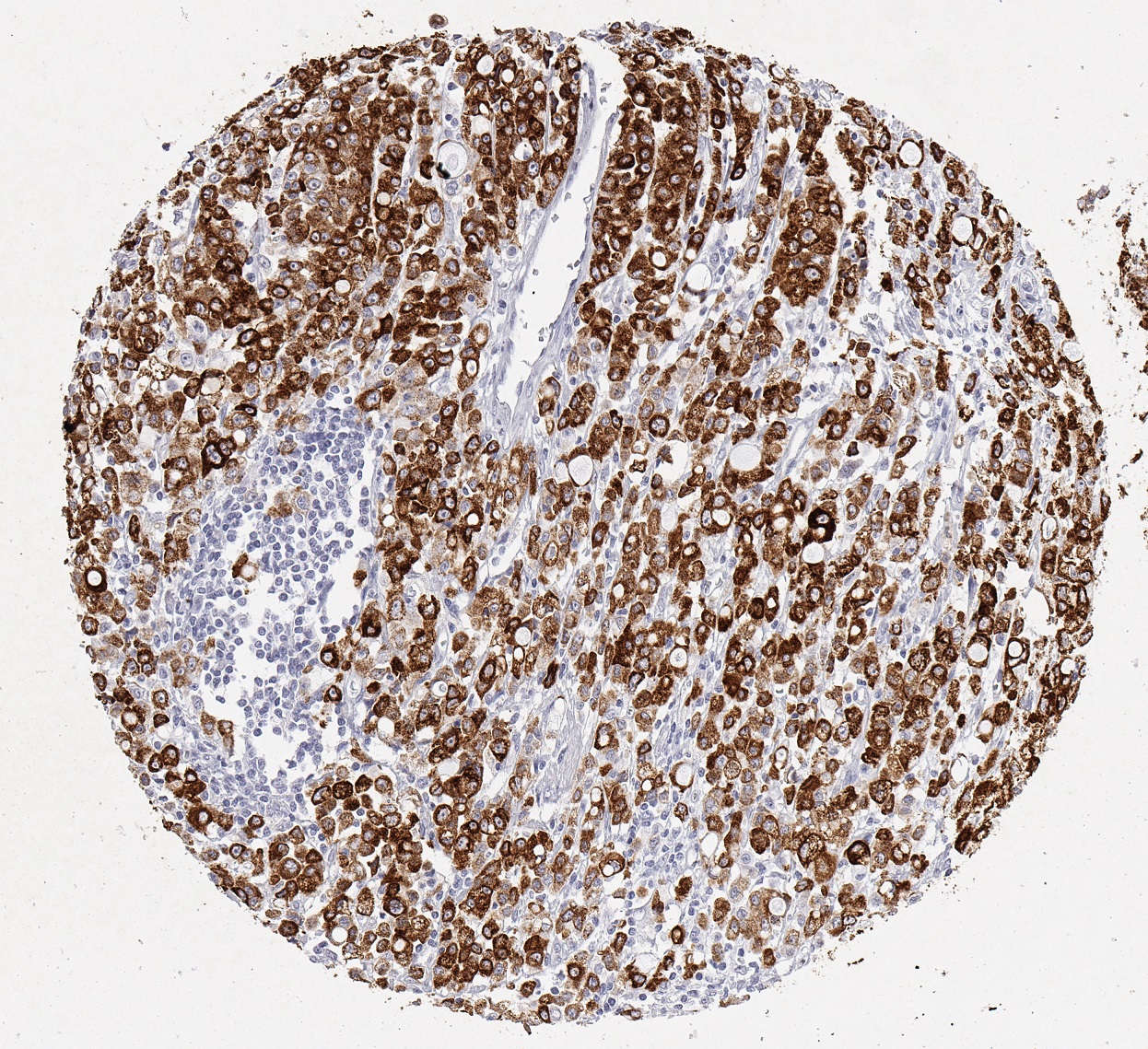
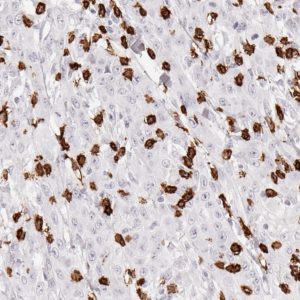
Clone JAC5 has been validated specifically for routine immunohistochemical (IHC) detection of MUC5AC in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue specimen.
Mucin 5AC glycoprotein (MUC5AC) is secretory-type mucin with 641kDa. Mucins are high molecular weight glycoproteins produced by epithelial cells and can be divided into two families; secretory mucins and membrane bound mucins. MUC5AC is highly expressed in surface mucosal cells of respiratory tract and stomach epithelia as a mucus-forming secreted, but not in normal colon cells. A number of carcinomas overexpress MUC5AC. MUC5AC expression is indicated in carcinomas wherein the type is defined as diffuse and infiltrative, and in carcinomas located mainly in the antrum. Moreover MUC5AC expression is correlated with colorectal signet-ring cell carcinoma: Overexpression of MUC5AC relates to the carcinogenesis, malignant potential, progression, and clinical behaviors. MUC5AC expression is present in primary ovarian mucinous cancer but usually absent in colorectal adenocarcinoma, thus showing an expression pattern opposite to MUC2.
Anti-MUC5AC may be useful for identification of intestinal metaplasia as well as in the identification of pancreatic carcinoma and pre-cancerous changes vs. normal pancreas. MUC5AC antibodies may also be useful for differential identification of primary mucinous ovarian tumors from colon adenocarcinoma metastatic to the ovary.